Yuang Ma, Bo Gou, Yuetong Xu, Muya Shu, Falong Lu, Xiang Li.
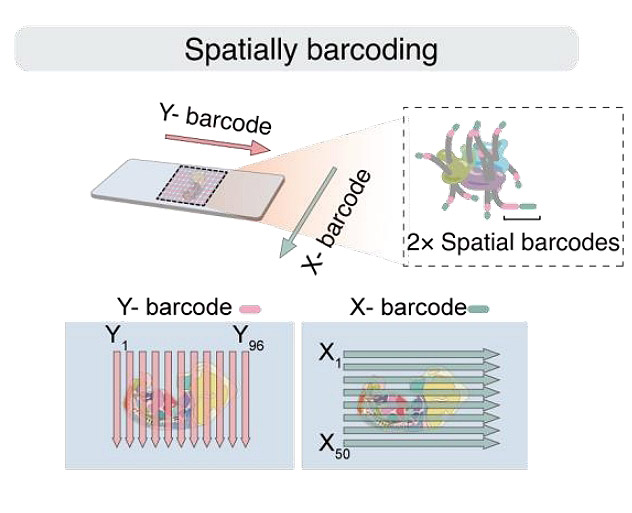
The 3D architecture of the genome is crucial for controlling gene expression and organ development. Here, we introduce a spatial 3D genomics approach for assessing chromatin conformation in-situ in tissue sections, by integrating microfluidic deterministic barcoding and SPRITE procedures. This method was applied to mouse embryo sections, revealing a hierarchical model of chromatin interactions within and between compartments in various organs. The intra-compartment interactions vary among organs to orchestrate gene expressions, while the inter-compartment interactions remain identical in the most organs. Beyond this, the liver exhibits overwhelmingly packed chromatin with enhanced adjacent-compartment interactions, possibly related to its physiology. These findings highlight the importance of tissue-spatial information in understanding embryonic chromatin organization. The approach presents a powerful tool for investigating these processes in tissues with high heterogeneity.